DISCO-2 is designed by students from Aarhus University and the IT University of Copenhagen and was initially a 2U cubesat of 10x10x20 cm. During vendor-negotiations the satellite size increased to 3U (10x10x30cm).
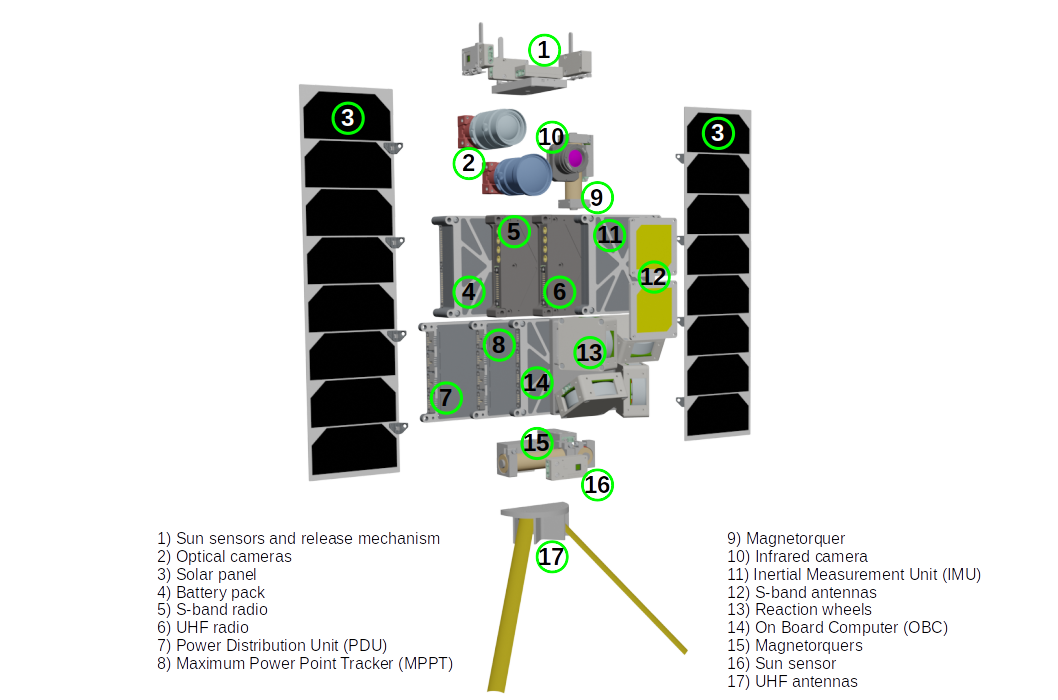
The satellite itself contains:
- Expandable UHF antennas for communication with the ground station for satellite control
- S-band patch antenna and potentially x-band patch antenna for high bandwidth downlink
- Multi-band radio for communication via antennas to and from the ground station
- Power system consisting of battery and solar cells mounted on the satellite itself and on expandable solar panels
- Redundant computer system for command execution and control and monitoring of systems on board.
- Attitude control system consisting of reaction wheels, magnetorquers and temperature, magnetic field, rotation and solar sensors.
- Payload consisting of cameras and control parts:
- Optical camera with wide-field lens for exact location verification, large scale mapping etc.
- Optical camera with zoom lens for high-resolution images of the earth's surface for the study of, glaciers, snow cover, icebergs and much more.
- Optional: An infrared camera.
- Control boards for interface between satellite OBC and cameras