Work Package 5
Modelling, Mapping and Machine Learning
Modelling and machine learning for reconstructing archaeology
This work package will integrate the data from WPs 1–4 into a set of predictive models which will allow patterns detected in one study area to be tested in similar contexts within other study areas. These models will incorporate machine learning solutions, traditional archaeological data, climate and sea level models and seismic geophysics in order to discover the differences and similarities between the archaeological records across the submerged landscapes of NW Europe. This work will proceed in close coordination with the work of WPs 1–4 so that results can be fed back into field expeditions and research cruises.
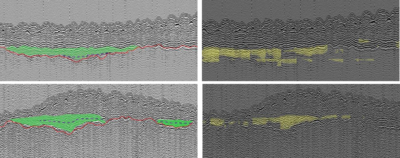
As data gathering technology has improved, data processing and integration have become the main challenges. Large amounts of heterogeneous data must be turned into workable models with falsifiable hypotheses to be tested with new data collection strategies. Artificial Intelligence (AI) can process seismic data at a speed and scale impossible when using traditional techniques of analysis. AI has proven its efficiency in many areas of research where (a) data are too extensive to be processed by hand, (b) direct access is restricted or too vast in scale and c) resources are limited and investigation is costly in either money or time. Submerged landscape archaeology is characterized by all of these problems. Potential areas of archaeological interest are inaccessible and often investigated following chance discovery of archaeological materials. Traditional coring and survey work in these conditions requires expensive boat time and must be optimally located to ensure an archaeological return.
Alongside landscape interpretation, data downscaling allows creation of landscape simulations which operate at human scales of days and weeks rather than traditional archaeological time scales of hundreds or thousands of years. This allows simulations that can better reflect interactions between humans and their environment at a scale similar to those which leave traces in the archaeological record. Sea level, climate, environmental and archaeological data will be combined to incorporate models of the behaviour of human inhabitants of the submerged landscapes, and the traces they would have left.